High Nitrogen Stainless Steel Properties

1 to investigate the possibility of producing high nitrogen martensitic stainless steel corresponding to the aisi 420 steel under atmospheric pressure by using gas nitrogen injection in the melt or by addition of fe cr n master alloy.
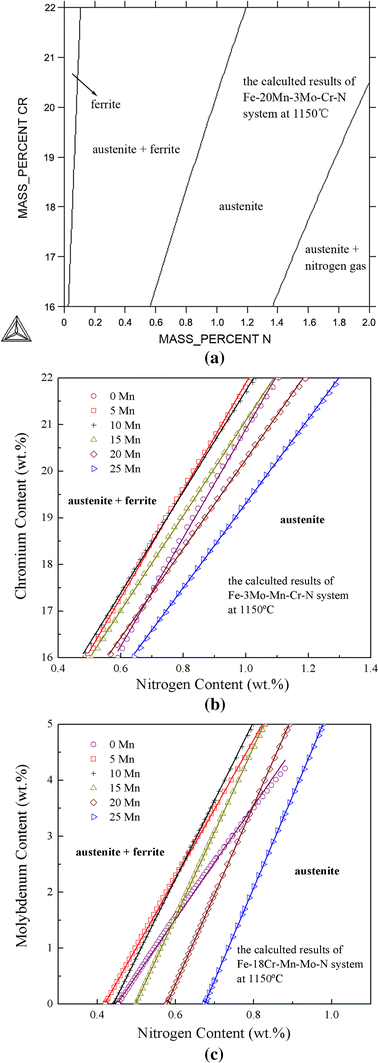
High nitrogen stainless steel properties. Austenitic steels are divided into the 300 series and 200 series subcategories which are determined by which alloys are used. High nitrogen stainless steels are not new types of stainless steels but their consumption is increasing. High nitrogen martensitic stainless steel shows improved resistance to localized corrosion like pitting crevice and intergranular corrosions over their carbon containing counterparts. Nitrogen can be a suitable substitute for nickel.
It contains nitrogen in the range 0 8 0 9 and has minimum 48 pitting resistance equivalent number pren. So the role of nitrogen and chromium is different with respect to corrosion resistance. The latter has a high relative price deleterious effect on mechanical properties and is allergenic and probably carcinogenic. The processing properties of the material are improved by adding sulfur.
Perhaps the most common category of stainless steel austenitic grade steels are high in chromium with varying amounts of nickel manganese nitrogen and some carbon. In general however most steel products require that nitrogen be kept to a minimum. Yes nitrogen is useful in improving corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Alloy af932n uns s31010 is the latest evolution of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels.
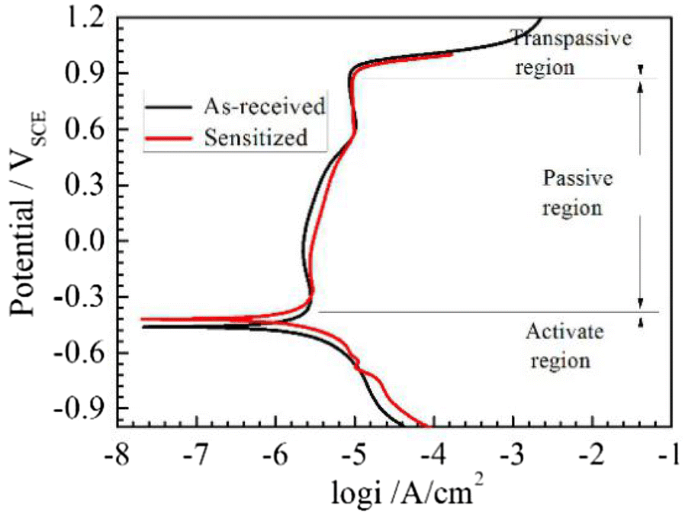
It is very useful in improving crevice and pitting corrosion resistance. Because of this the high nitrogen steel are considered as new promising class of engineering materials. Also discussed but as a secondary consideration are the corrosion resistance qualities of stainless steels at elevated temperatures. 420 stainless steel blade grade martensitic steel the earliest stainless steel similar to brinell high chromium steel.
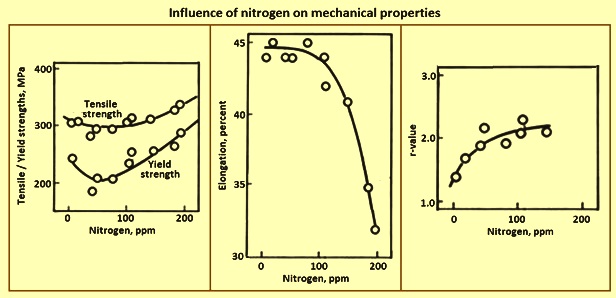
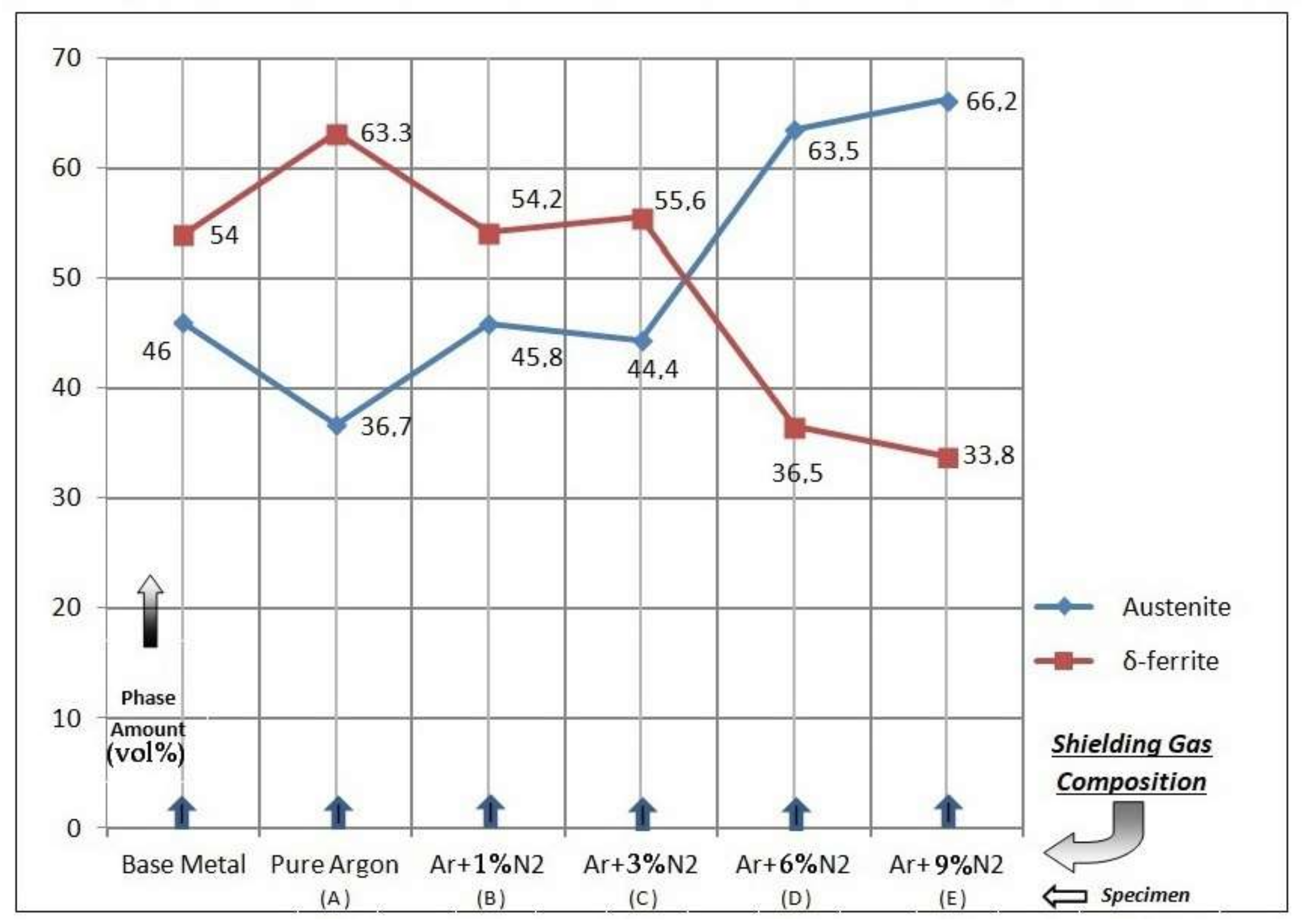
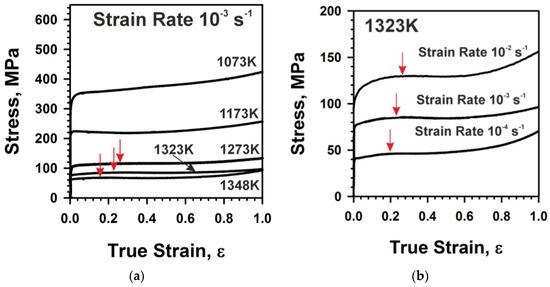
The magnetic permeabilities achievable in austenitic stainless steels are very low compared with conventional magnetic materials such as silicon iron alloys. High nitrogen content may result in inconsistent mechanical properties in hot rolled products embrittlement of the heat affected zone haz of welded steels and poor cold formability. This alloy is produced by air melting followed by aod argon oxygen decarburization refining in a vessel of 70 tons capacity thus providing ingots up to 25 tons from which components up. The characteristics that make some of the stainless steels particularly useful in high temperature environments are described and typical engineering data are presented.
2 to compare the mechanical properties and corrosion.