Height Of Geostationary Satellite Formula

Through the use of re arranging the above equation we can come to the equation.
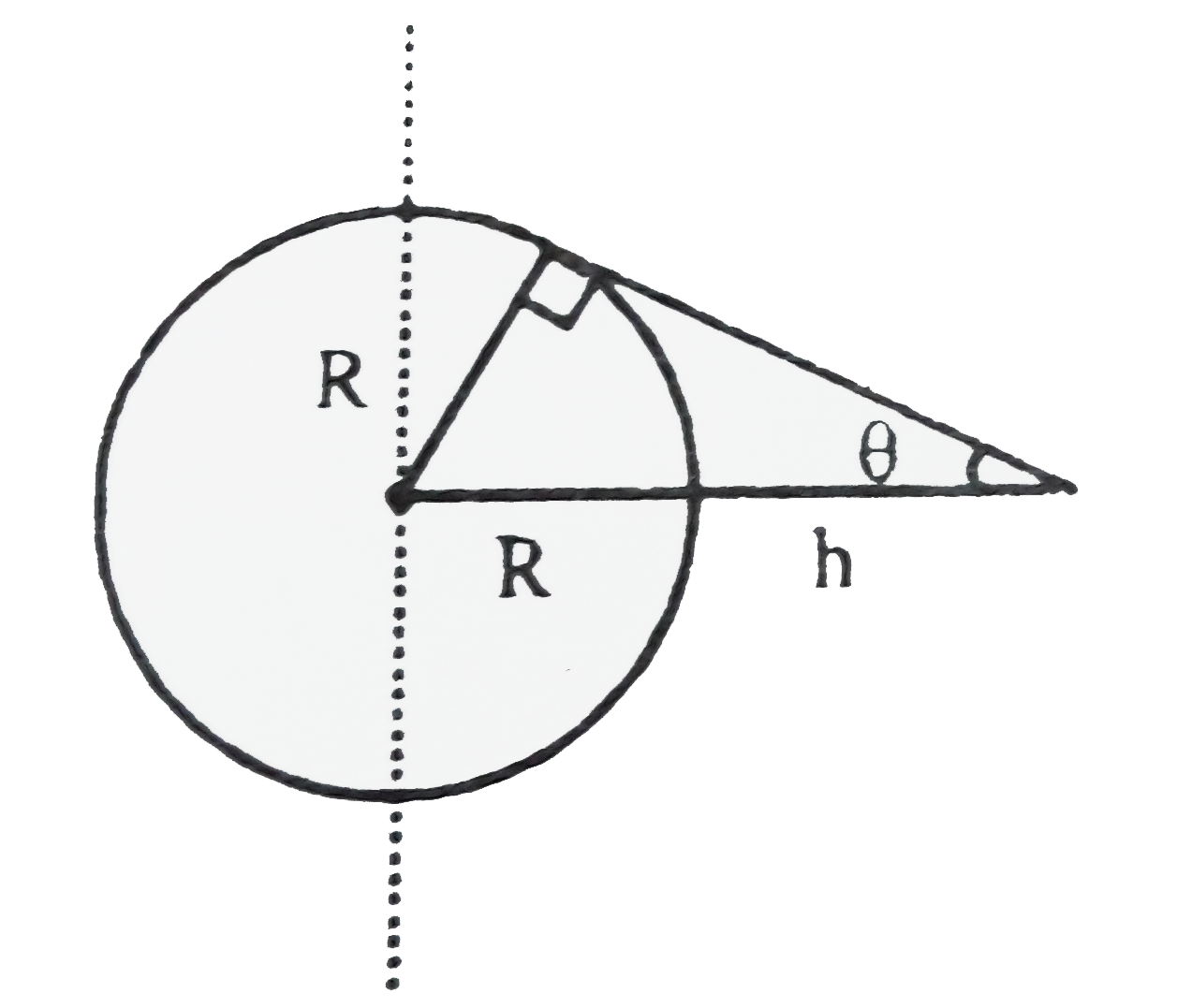
Height of geostationary satellite formula. So the height of the satellite is 3 59 x 10 7 m. Now that the radius of orbit has been found the height above the earth can be calculated. We can calculate the height h above the earth s surface by subtracting the radius of the earth from the radius of the orbit. 4 23 x 10 7 m 6 37 x 10 6 m 3 59 x 10 7 m.
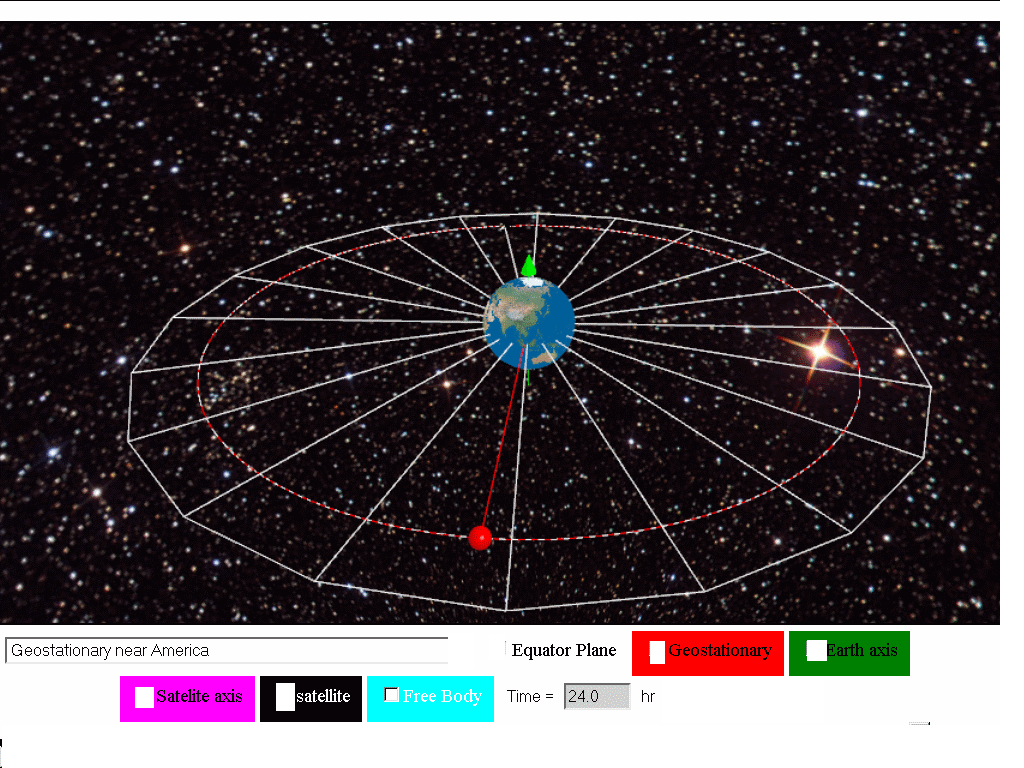
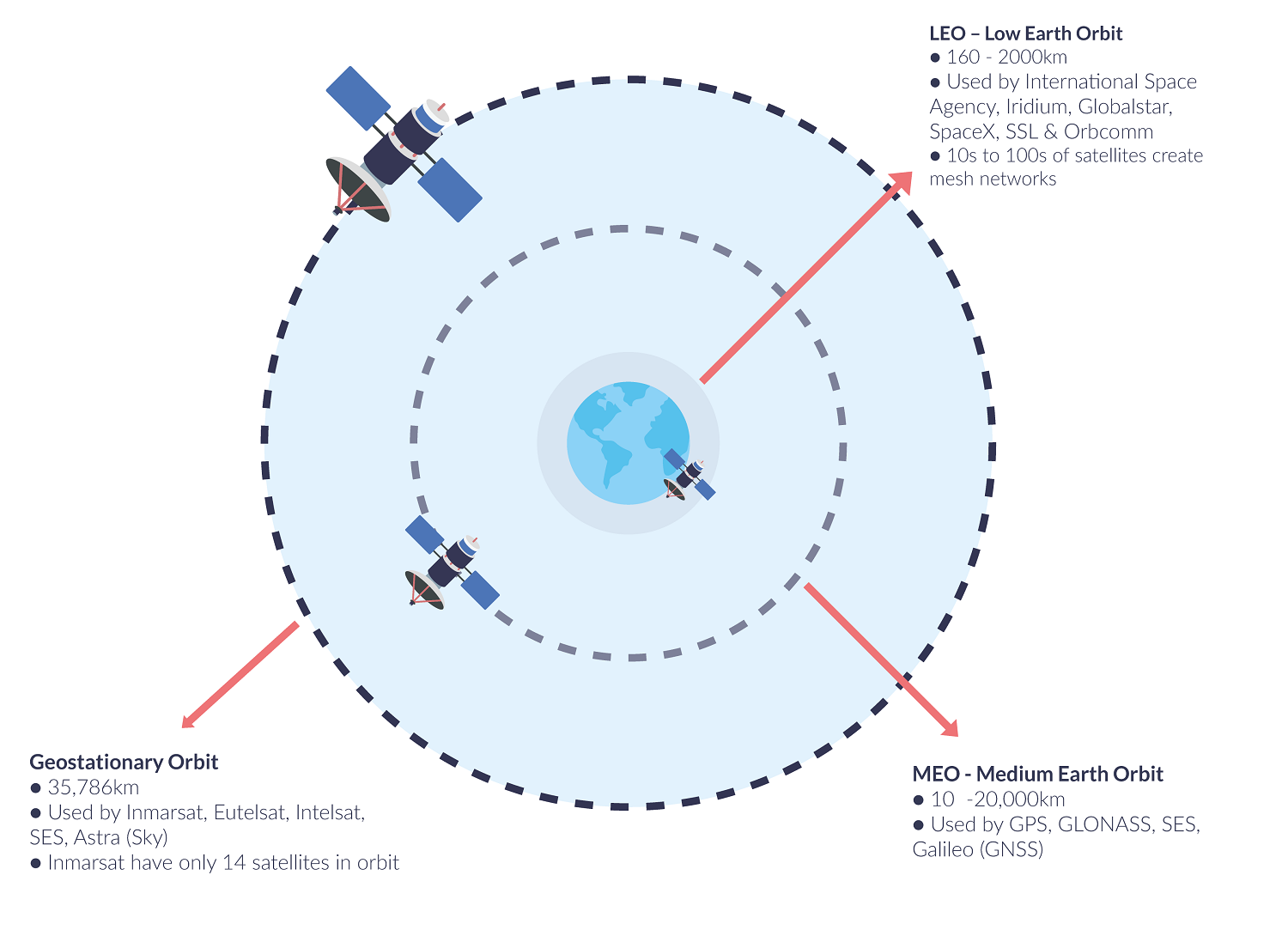
Since the earth s surface is 6 37 x 10 6 m from its center that s the radius of the earth the satellite must be a height of. A geostationary orbit also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit geo is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35 786 kilometres 22 236 miles above earth s equator and following the direction of earth s rotation. From earth they would seem drifting in westerly direction. Enter your latitude and longitude and our geostationary satellite calculator will compute the satellite elevation azimuth and range from each satellite to your position.
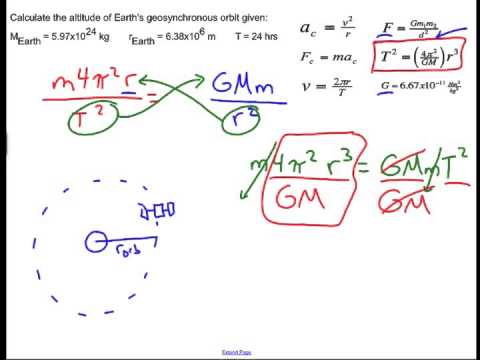
H 4. Shows how to calculate the orbital height of a satellite above the surface of the earth. Where g 6 67384m 3 kg s 2 is the gravitational constant m 5 972 10 24kg is the mass of the earth m is the mass of the satellite and r is the distance from the centre if the earth to the satellite. The height of a geostationary orbit is calculated as the distance required to have an orbital period of 24 hours.
The force of gravity acting on a satellite is given by the formula f gmm r 2. The radius of the earth is 6 37 10 6 m. Above the surface of the earth. The equation assumes that the satellite is high enough off the ground that it orbits out of the atmosphere.
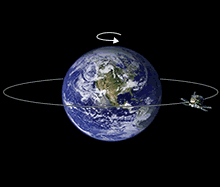
R g m2 t 4π we know that m2 is the mass of the earth at 5 98 10 24 kg t is the time period and g the universal gravitation constant at 6 67 x10 11 kg 2. The height of the geostationary orbit is 35786 kilometers above earth in geostationary orbit the satellite moves with an orbital speed of 11068 km per hours. A geostationary satellite is a satellite in geostationary orbit with an orbital period the same as the earth s rotation period. To calculate the radius of a geostationary orbit the centripetal force must equal the gravitational force on the satellite or mass.
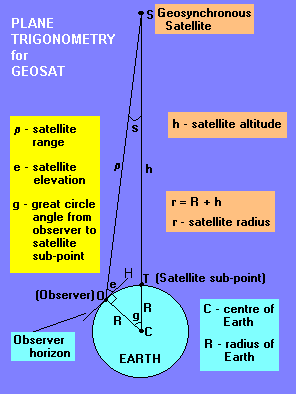
In this case you add the distance from the center of the earth to the surface of the earth 6 38 10 6 meters to the satellite s height above the earth. A minimum of three satellites are needed to cover the entire earth super synchronous orbit is a disposal storage orbit above gso.