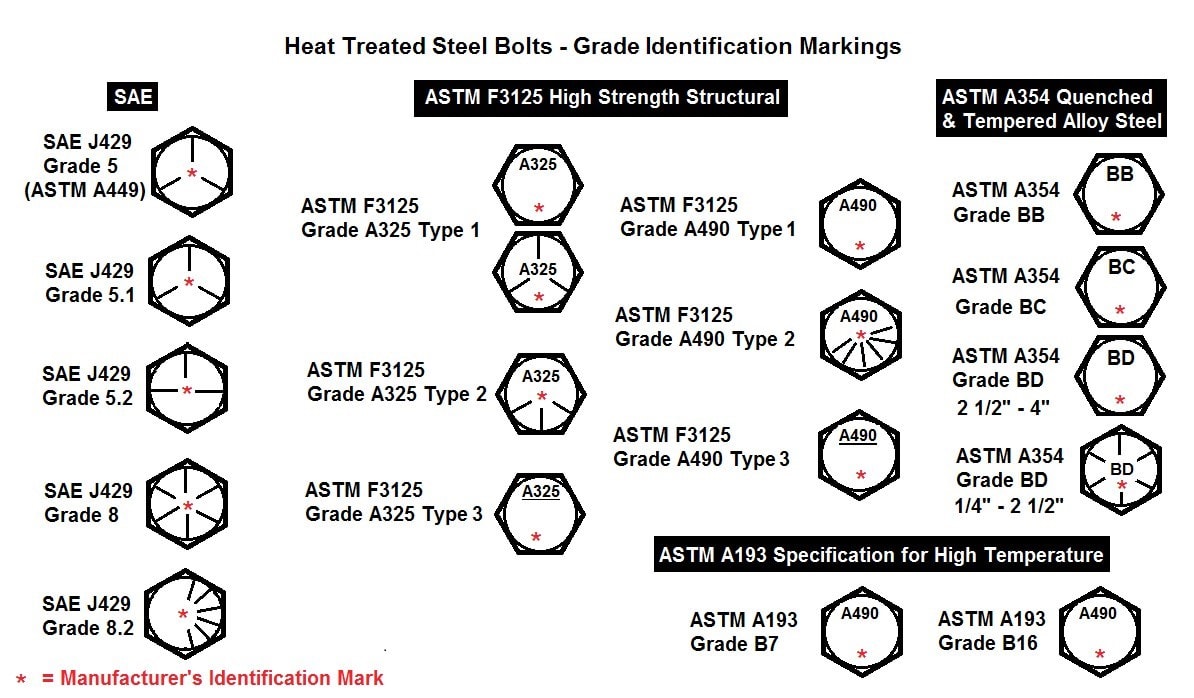
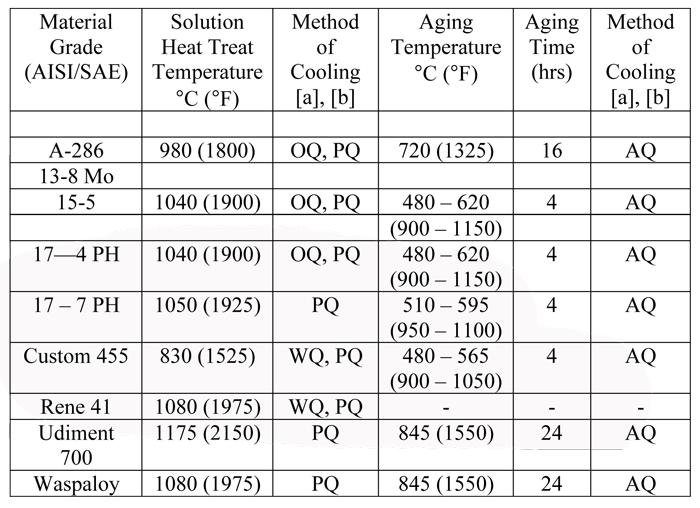
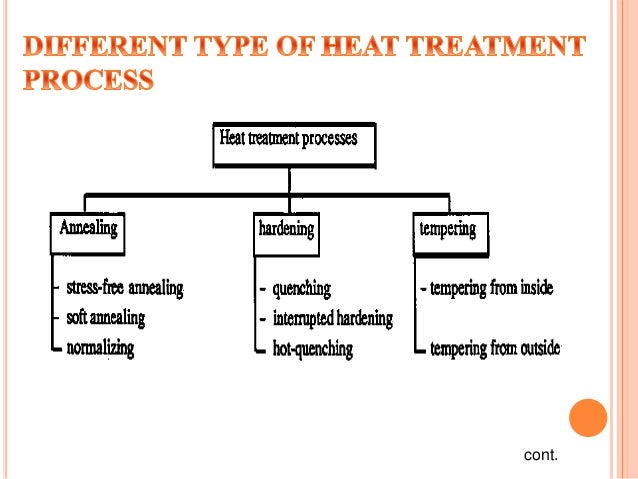
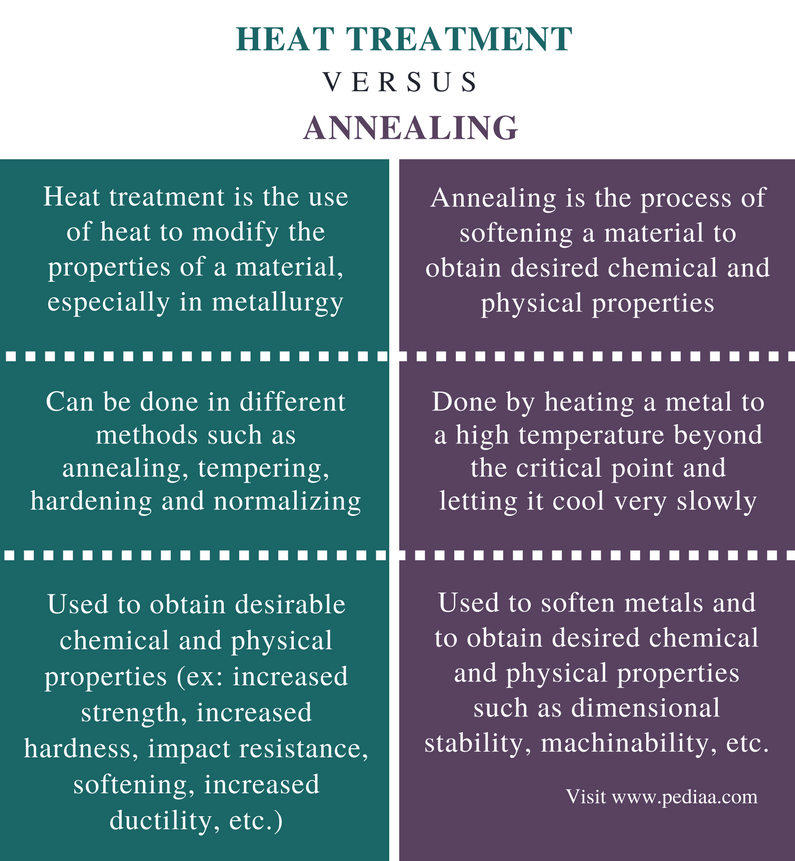
Heat Treatment Procedure For Steel Tempering
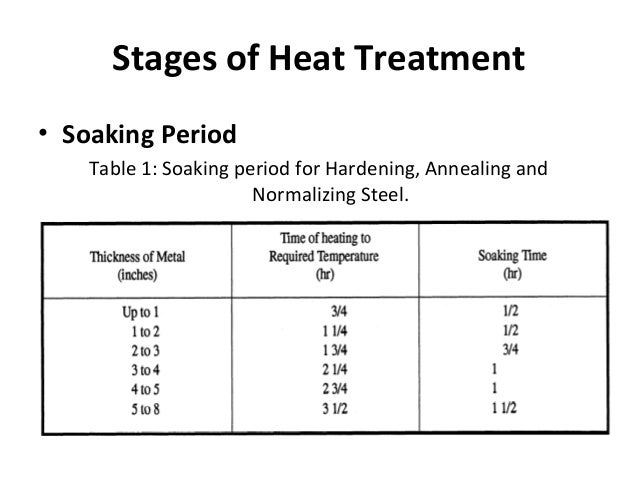
It s hard to predict the optimal heat treatment of one steel based on the results of another.
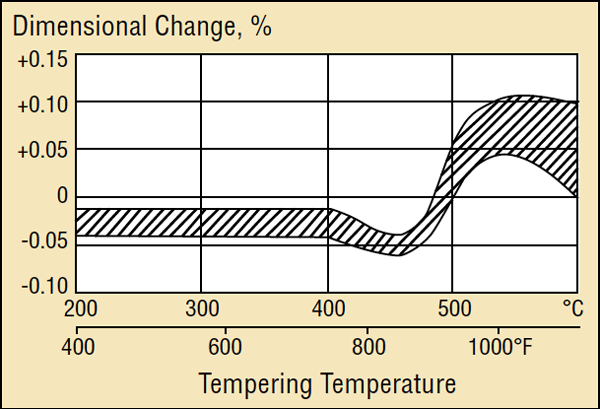
Heat treatment procedure for steel tempering. Heat treatment is the single most important factor in determining performance of the steel. These alloys are more formally called steel. Sae 1040 steel standard charpy type impact specimens will be used. The tempering changes in hardness as a function of tempering temperature where tempering time is kept constant of 1 hour at each temperature.
The reduction in hardness is usually accompanied by an increase in ductility thereby decreasing the brittleness of the metal. For a given steel a heat treater might like to choose some convenient time say over night or otherwise different than 1 hour and thus wants to calculate the exact temperature required to achieve the. Some steel specific annealing heat treatments include normal izing spheroidizing and solution annealing which is described as follows. The datapoint for 8670 toughness on the chart in the article came from 1525 f for 10 minutes quench in dt 48 oil then tempered at 400 f.
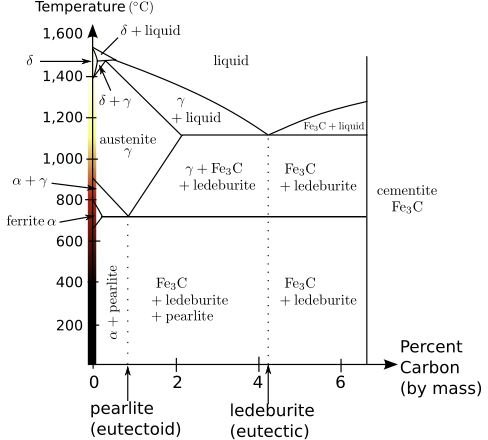
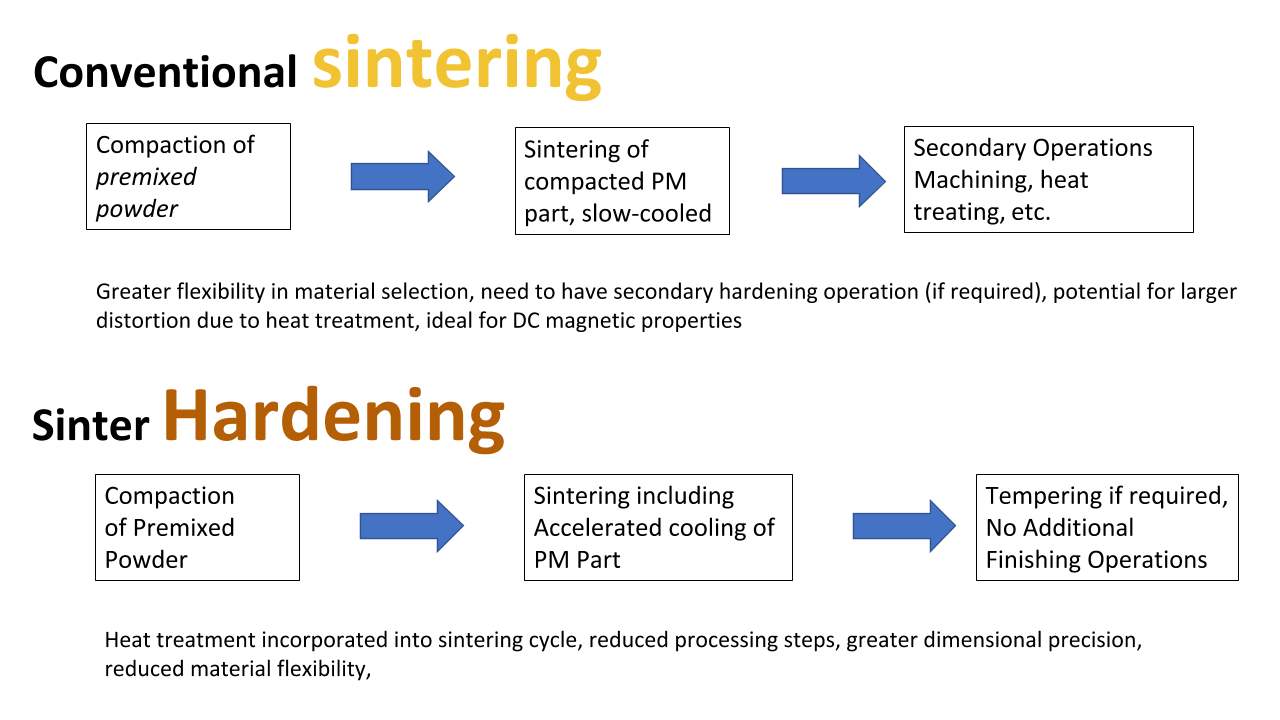
In general the process for heat treating steel is accomplished by heating rapid cooling and reheating of the chosen material. The heat treatment is called solution annealing because the heat treatment takes. The challenge for the customer is determining whether a proper heat treatment has been performed. Solution annealing sometimes referred to as quench anneal ing is an important category of annealing.
Tempering is a type of heat treatment for iron carbon alloys. When a steel has to become very hard it is only tempered at relatively low temperatures in the range of 200 c to 400 c while it becomes tougher and high load capacity at higher. Tempering heat treatment process classification of tempering. There was no cryo treatment.
Tempering is a heat treatment technique applied to ferrous alloys such as steel or cast iron to achieve greater toughness by decreasing the hardness of the alloy. After it has cooled ts to 120 f the workpiece must be loaded immediately for the first tempering cycle. The loss of carbon from the steel s surface during the heat treating cycle. If high carbon steel is quenched for hardening in a bath it becomes extra hard extra brittle and has unequal distribution internal stresses and strain and hence unequal harness and toughness in structure.
When steel is cooled quickly the atoms are frozen in an unstable position. Tempering is usually performed after quenching which is rapid cooling of the metal to put it in its. That heat treatment led to nearly 60 rc and high toughness. Heat treatment quenching tempering objectives 1 to investigate the conventional heat treatment procedures such as quenching and annealing used to alter the properties of steels.












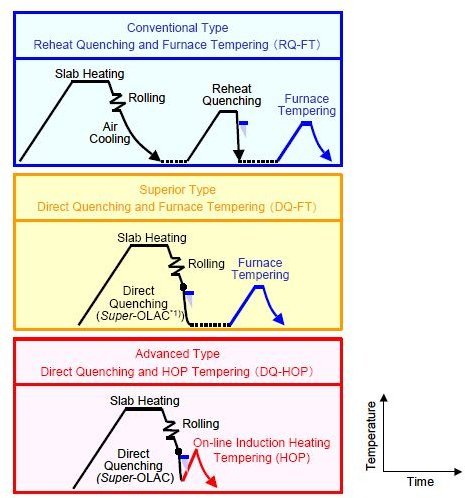
























/stories/2018/07/43628.jpg)